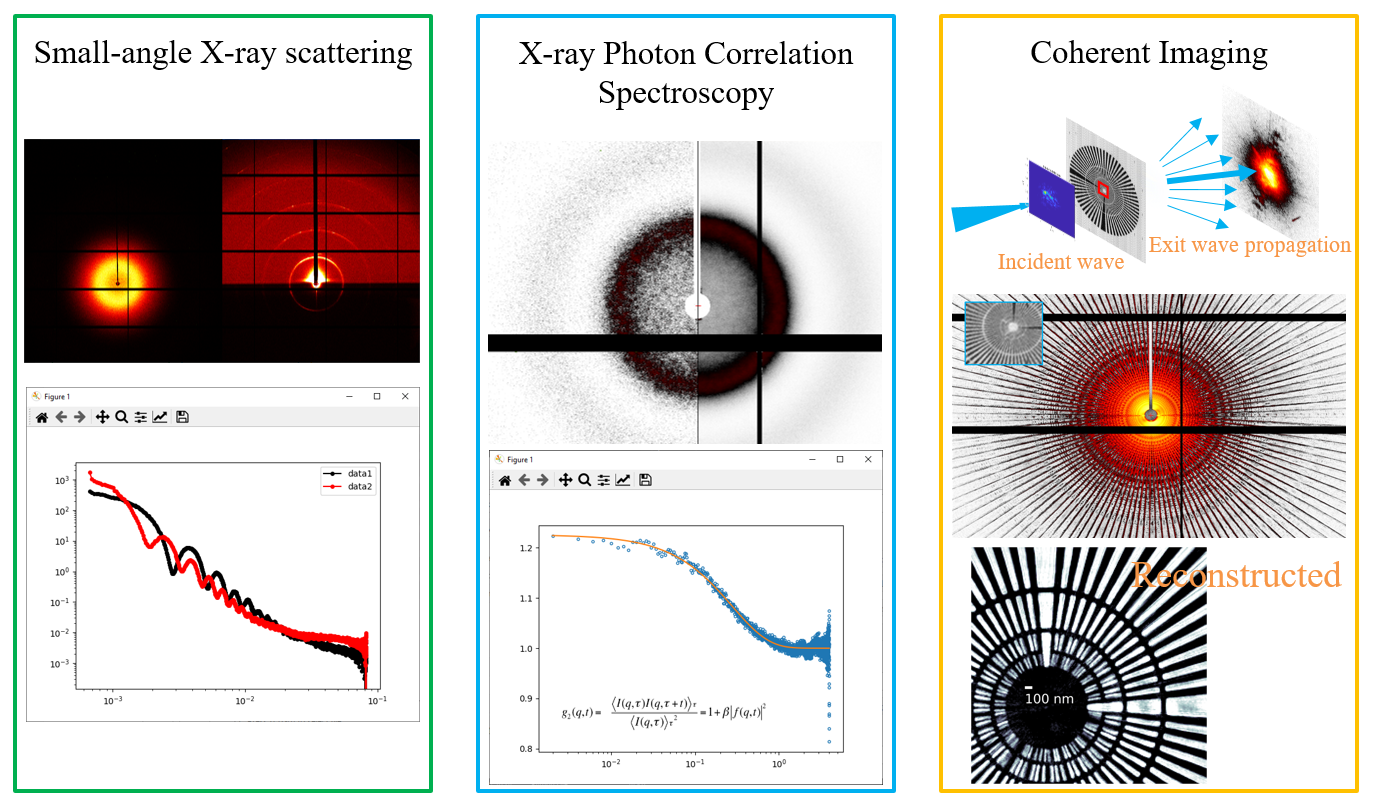
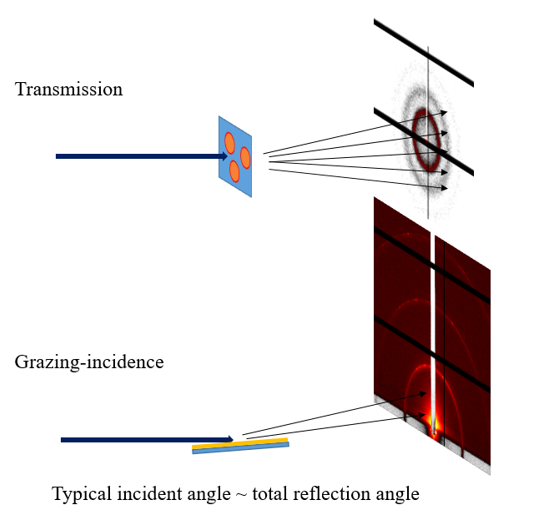
Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) / Grazing-incident SAXS (GISAXS)
SAXS: probing the nanoscale structure of bulk and liquid samples.
GISAXS: probing in-plane (Qxy) and out-of-plane (Qz) nanoscale structure of the thin film samples.
The reciporcal-space scattering pattern from the sample is the 3D Fourier transform of the real space of the sample. For the sample with the periodic structure, the data will show the structure factor or correlation peaks at q = 2π/d. For the diluted system, there is no interference between the scatters, and the data shows the form factor of the scatters. In most cases, you will get the data of the form factor together with the structure factor (i.e. I(q) = nS(q)P(q)). It need to do the model fitting to obtain the quantitative properties of the sample.
Coherent Scattering
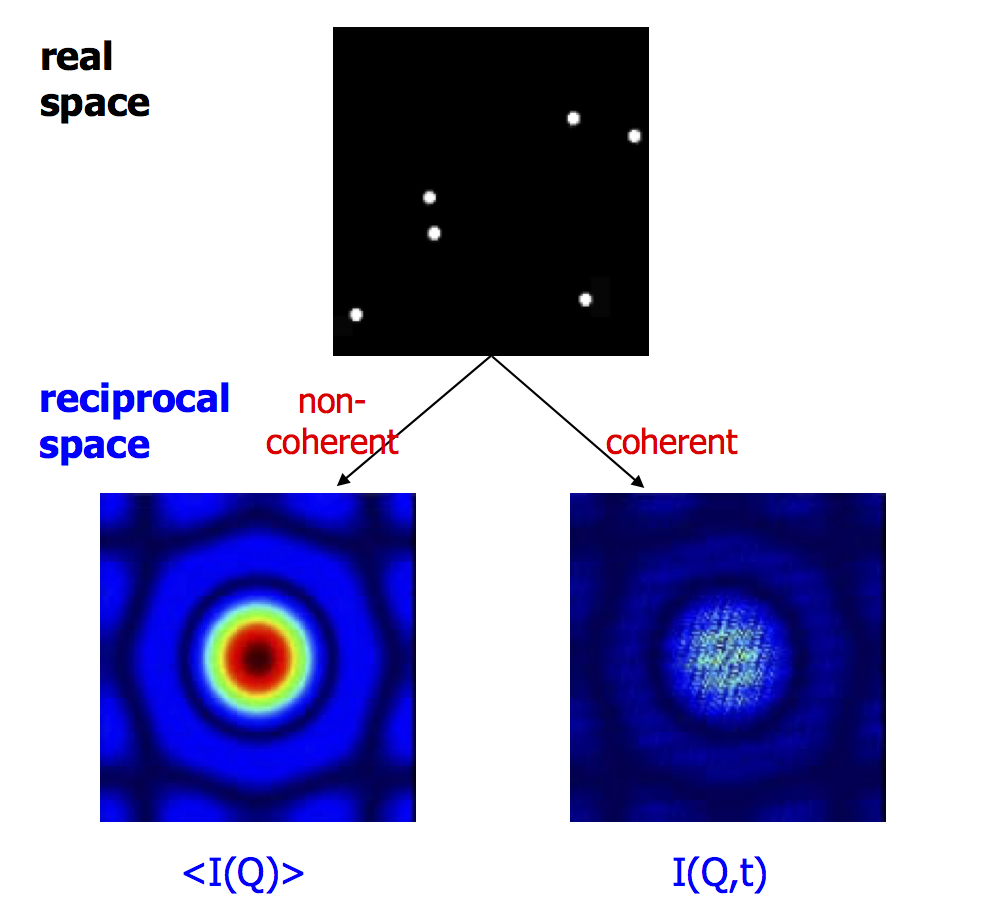
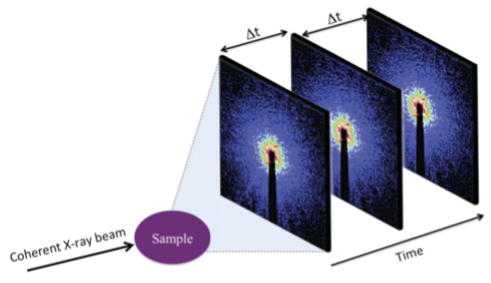
X-ray Photon Correlation Spectroscopy (XPCS)
XPCS measures the temporal changes in speckle patterns produced when coherent light is scattered by a disordered system.
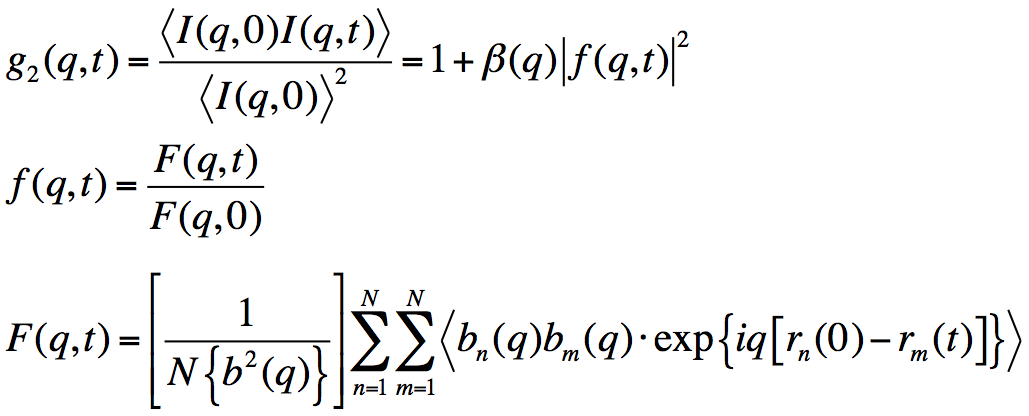
J. Synchrotron Rad. 21, 1057–1064 (2014)
The XPCS experiments are collecting time-resolved speckle patterns from the same coherent volume. With doing the correlation function between the frames of speckle patterns, one can obtain g2(q,t) and two-time correlation function from the dataset. If diagonal components of two-time correlation function are the similar values, this system may not have higher-order correlation time.
Coherent Diffraction Imaging (CDI)/Ptychography/Bragg CDI
CDI/Ptychography – Reconstructed structure of non-crystalline samples
Bragg CDI/Bragg Ptychography – Resolving the local strain and defect within crystals (phase images)
CDI phase retrieval algorithm (HIO)
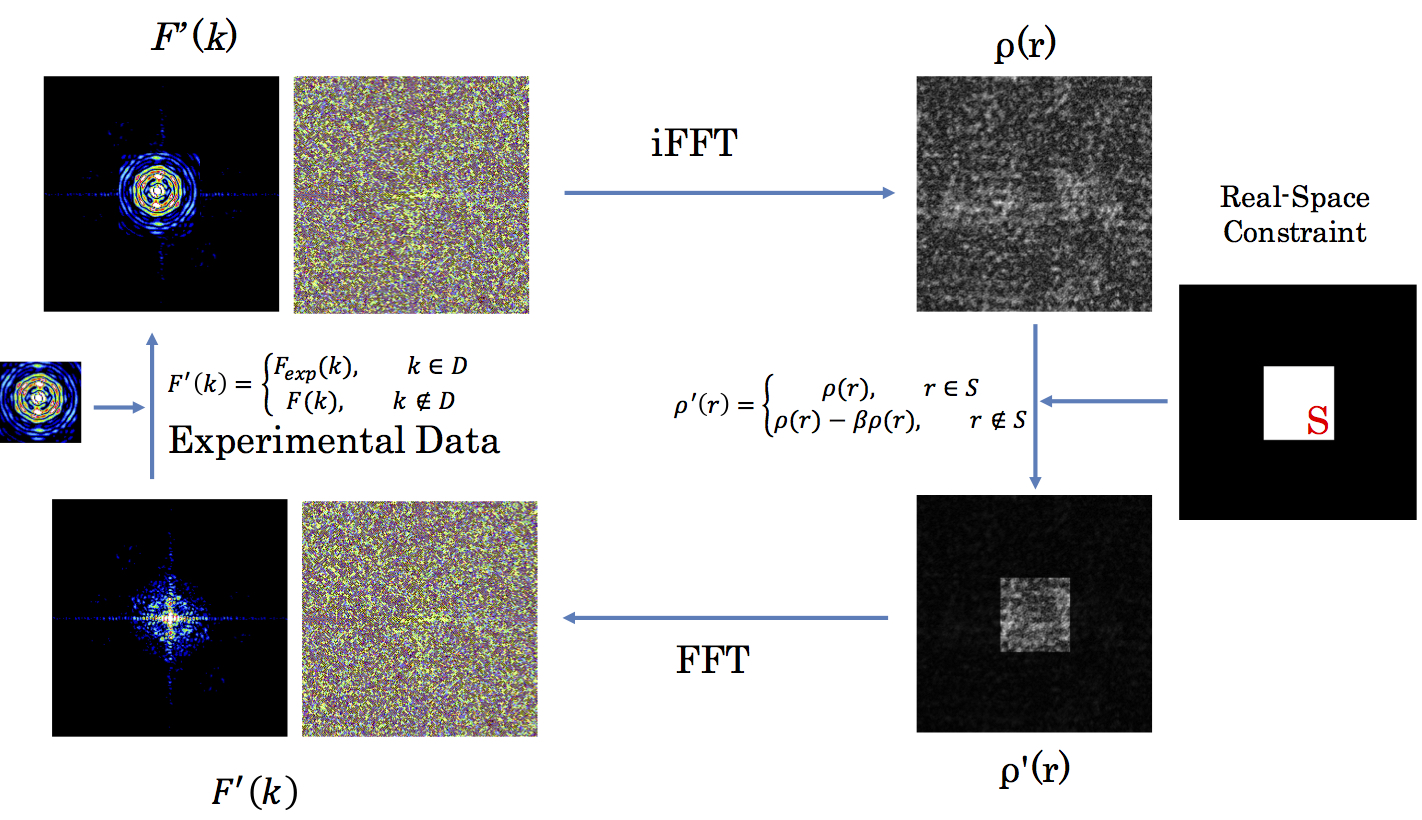
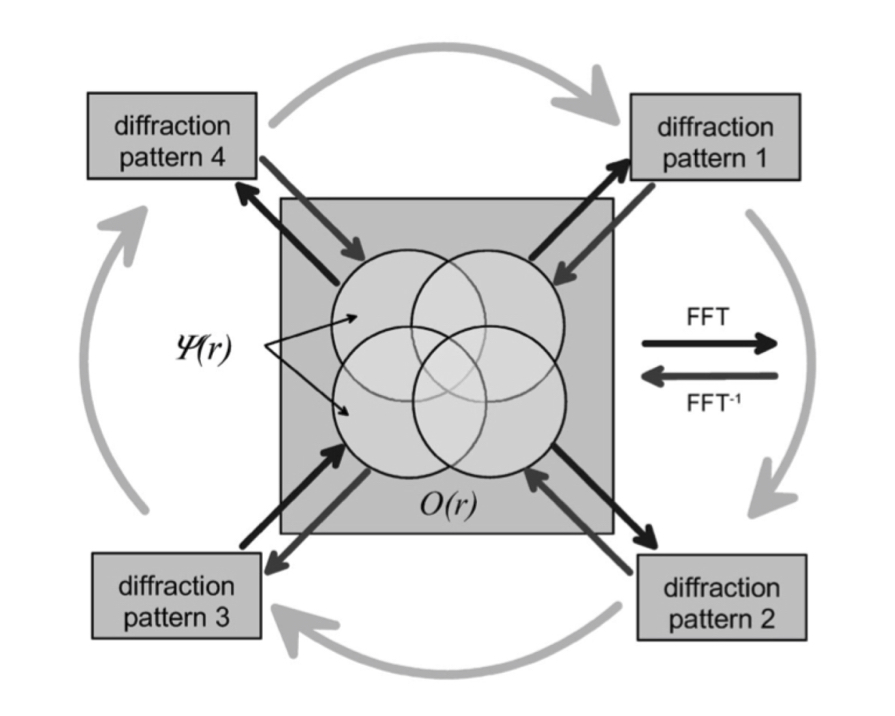
Ptychographic Iterative Engine (PIE)
J. M. Rodenburg et al, PRL 98, 034801 (2007)
Real-space support: the redundancy or the overlapped regions
Reciprocal-space support: experimentally collected intensities